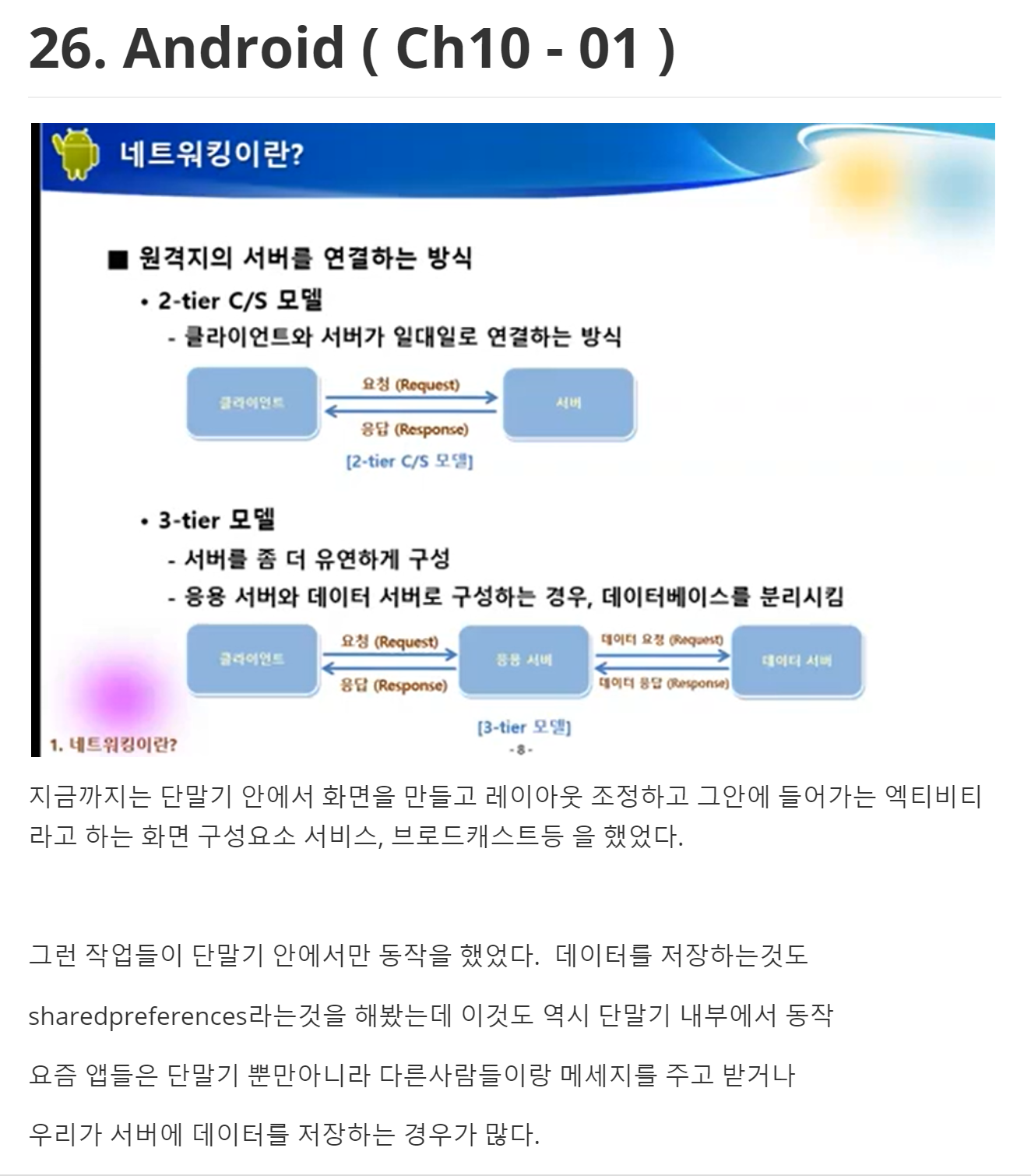
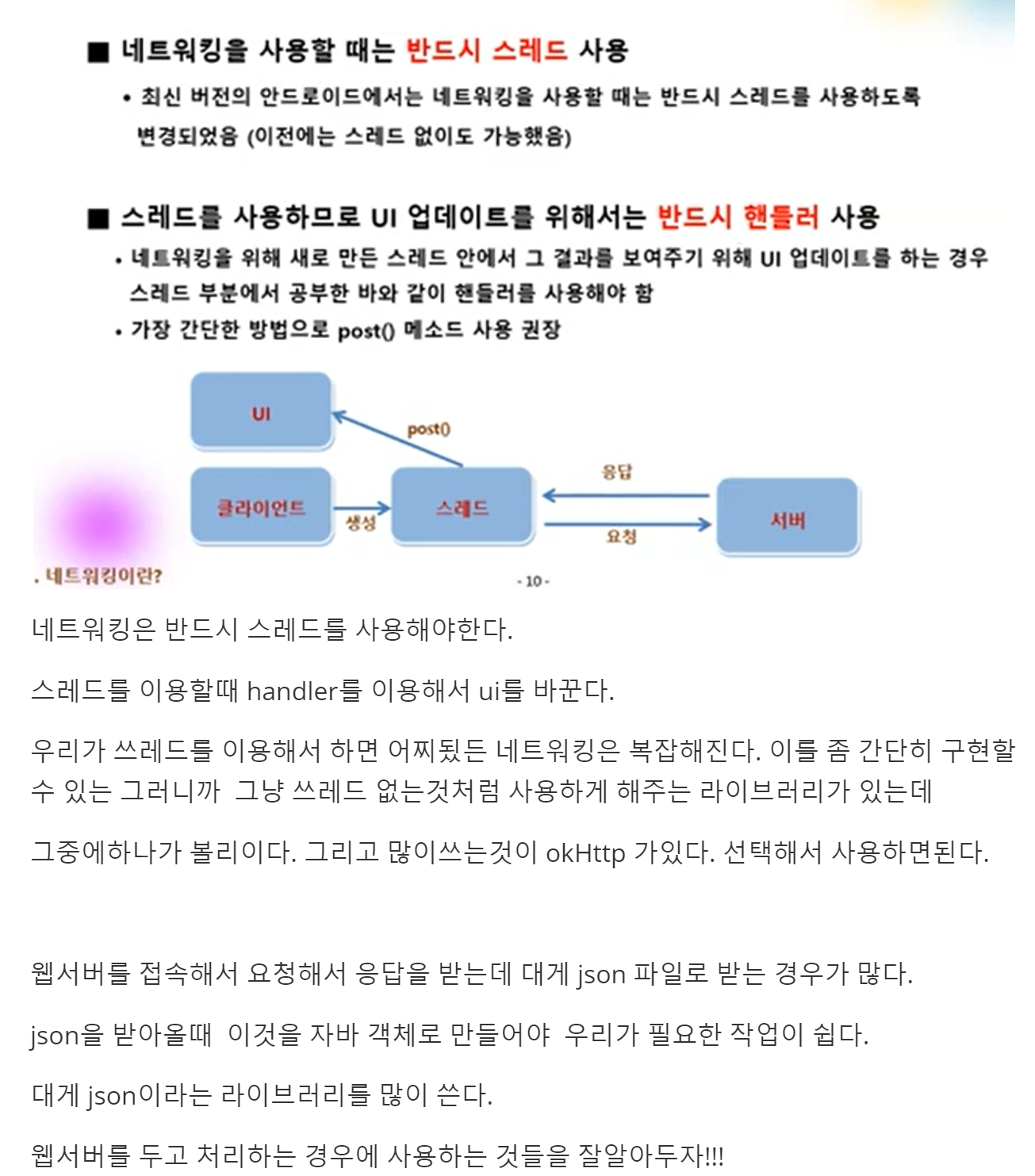
728x90
반응형


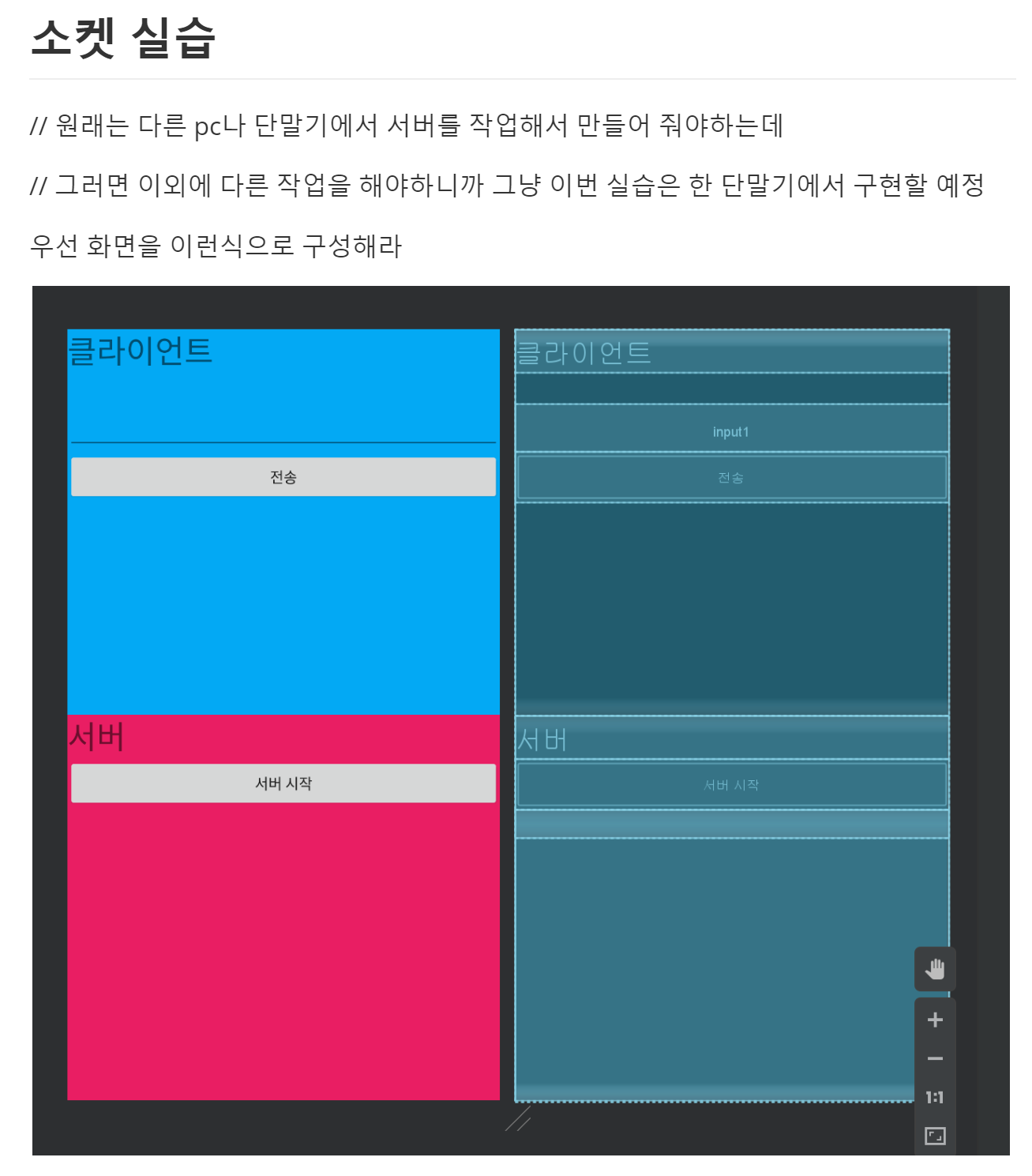
**activity_main.xml**
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#03A9F4"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:text="클라이언트"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/input1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/sendButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="전송" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:background="#E91E63"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="30sp"
android:text="서버"
android:textSize="30sp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/startSeverButton"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="서버 시작" />
<ScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/output1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="20sp" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>//서버라는것은 우리가 버튼을 눌렀을때 서버를 시작하게 할 수 있다.
물론 그냥 자동으로 시작하게도 할 수 있다.
**MainActivity.java**
package com.threedpit.mysocket;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.io.Externalizable;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.logging.SocketHandler;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
EditText input1;
TextView output1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
input1 = findViewById(R.id.input1);
output1 =findViewById(R.id.output1);
Button sendButton = findViewById(R.id.sendButton);
sendButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
final String data = input1.getText().toString();//사용자가 입력한 값 가져오기
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
send(data);//데이터 서버로 보내는 메소드
//네트워크 부부은 쓰레드 사용, 권한 설정, 쓰레드를 사용해 ui 갱신시 핸들러 사용 생각하자
}
}).start();//.start()하면 run 메소드가 실행됨
}
});
Button startServerButton = findViewById(R.id.startSeverButton);
startServerButton.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
startServer();
}
}).start();
}
});
}
public void startServer(){//서버 실행 코드 ,서버란 대기하기 위한것이다
int port = 5001;
try{
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);//서버는 자긴 자신이 특정 해당위치에 있기때문에 포트만 하지만 필요한 경우 ip도 같이한다.
while(true){
Socket sock = server.accept();//이것은 서버가 계속 대기하다가 클라이언트가 들어오면 이accept가 실행 여기서는 블로킹이라고 해서
//멈춰있다가 실행한다.
//클라이언트 쪽에서 연결한 소켓의 포트와 ip주소를 출력 해볼 수 있다.
InetAddress clientHost = sock.getLocalAddress();
int clientPort = sock.getPort();
println("클라이언트 연결됨 : "+clientHost+","+clientPort);
//서버쪽은 클라이언트와 반대다
ObjectInputStream instream = new ObjectInputStream(sock.getInputStream());
String input = (String) instream.readObject();
println("데이터 받음:"+ input);
//클라이언트 쪽으로 전송
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(sock.getOutputStream());
outputStream.writeObject(input+ "from server");
outputStream.flush();
println("데이터 보냄");
sock.close();;
}
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void println(String data){//데이터 로그 찍는 메소드드
output1.append(data+"\n");
}
public void send(String data){
//클라이언트 부분 소스
//HW적으로 본다면 단말기 내부에 이더넷이이 있다. 이더넷은 포트를 가지고 있는데 6만개넘은 것중에 하나를 사용해야한다.
int port = 5001;
//소켓으로 보내려면 소켓 연결을 만들어야한다.
try{
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", port);// 원래는 localhost가 아니라 연결한 단말기의 ip를 넣어야한다.
//그냥 선언하면 에러가 뜨기 때문에 혹시나 예외조건이 생길때 잘못됨을 방지하기위해 예외 처리 해준것
//데이터 전송시 아래와 같이 객체 생성해서 ObjectOutputStream로 감싼다.
//getOutputStream()은 자바의 i/o 부분이다.
//우리가 데이터를 네트워킹통해 보낼 때는 바이터레이로 주고 받음
//글자가 있으면 바이터레이로 바꾸고 바이터레이를 글자로 바꾸는 과정이 복잡하기 때문에
//글자나, 객체를 바이터레이로 바꿀때 쓸수 있는 기능을 자바에서 만들어 놓은게 있다.
ObjectOutputStream outstream = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
outstream.writeObject(data);//이런식으로 데이터를 쓸수 있다.
outstream.flush();//우리가 데이터를 inputStream, outputStream을 쓸때 버퍼라는것을 사용하는데
//버퍼는 한꺼번에 사용하는것이 아니라 통같은 곳에다가 채워질때까지 담아놨다가 채워서 보내는것이다.
//그래서 그런것들이 남아있는 경우가 있기 때문에 flush를 해주면 남아있는것을 전부다 출력을 하게 된다.
//서버쪽에서 데이터 받는경우 처리 해준것
ObjectInputStream instream = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
String input = (String)instream.readObject();
socket.close();//꼭 다사용을 했으면 닫아줘야한다.
}catch(Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
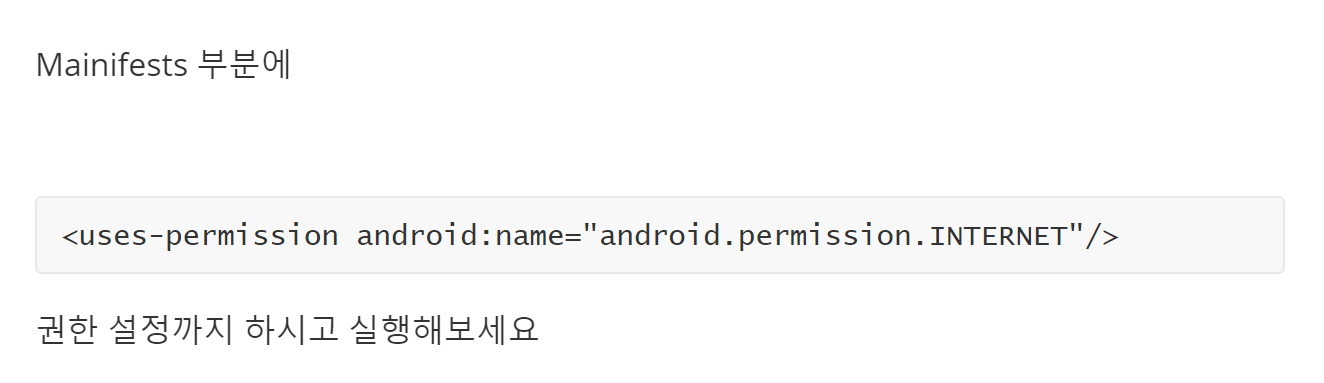


728x90
반응형
'안드로이드(Android)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 2021년09월14일_안드로이드1 (0) | 2021.09.16 |
|---|---|
| 안드로이드 이론 빡공 28 (0) | 2020.07.23 |
| 안드로이드 이론 빡공26 (0) | 2020.07.21 |
| 안드로이드 이론 빡공 25 (0) | 2020.07.20 |
| 안드로이드 이론 빡공 24 (0) | 2020.07.17 |



댓글